How to dynamically monitor biological cleanrooms
- 2024-12-11
- 1129
- Esky Purify
A cleanroom is a room in which the concentration of suspended particles in the air is controlled, and air cleanliness, temperature, humidity, pressure, noise, and other parameters are controlled as needed in a well-closed space. Divided into industrial cleanroom and biological cleanroom, biological cleanroom is concerned about the number of suspended particles in the air and bacterial plankton, the need for strict control, especially sterile pharmaceutical cleanroom, the need for real-time dynamic monitoring, equipped with real-time particle counters and bacterial plankton sampling instrument. So, what items need to be tested for dynamic monitoring and what are the corresponding standards?
1, the significance and role of the implementation of dynamic monitoring
In class A/B clean area, the implementation of dynamic monitoring is for the evaluation of personnel behavior, the final product release to provide the necessary basis for the timely detection of problems, and take timely and effective measures to solve the problem to prevent further expansion of the adverse effects, at the same time, but also for the air balance, personnel behavior and the room disinfection methods to provide a basis for further improvement.
2. Dynamic monitoring items and standards
2.1 Items to be monitored
Before the production operation, the temperature, humidity and differential pressure in the area should be checked and controlled;during the production process, the situation of settled bacteria, planktonic bacteria, suspended particles and wind speed should be monitored;after the completion of the key operation, the surface of the facilities and equipment and personnel hygiene should be monitored. At the same time, before and after the start of production, the isolation operation gloves should be tested.
2.2 Temperature and humidity monitoring
For example, mesophilic microorganisms grow best at 25 to 30 ℃;wet-born microorganisms grow and reproduce more vigorously in an environment with a humidity of 70% to 90%, so it is generally necessary to avoid this temperature and humidity range. At the same time, the temperature, humidity is too high or too low, the comfort of the human body, the personnel's working mood, etc. have a great impact, and then will also seriously affect the operation behavior of the personnel in the A/B level area, and can not effectively guarantee the safety of the product. In general, the temperature of the survival environment of sterile preparation should be controlled at 18~24 ℃, humidity should be controlled at 45%~65%.
2.3 Relative pressure difference monitoring
The air static pressure difference between clean areas of different cleanliness levels and between clean areas and non-clean areas should be more than 10Pa, and the device indicating the pressure difference should be installed;the production area which is prone to generate dust should maintain relative negative pressure with the neighboring room (area);between different functional areas (operation rooms) of the same cleanliness level, the appropriate differential pressure gradient should be maintained. At present, the commonly used differential pressure meter range between 0 to 60Pa, negative pressure differential pressure meter range is generally selected between -30 to 30Pa, so, in the daily production process, should be instruments, meters itself calibration or calibration to strengthen the supervision and management, because the differential pressure can increase the abnormal alarm situation. However, in order to avoid the alarm caused by normal operation (such as opening the door), the alarm delay device can be increased appropriately, and the specific delay time can be derived from the verification of the time required for opening and entering the door or material transfer and closing the door by different personnel.
2.4 Particle and microbial monitoring of the design of the clean zone must meet the appropriate cleanliness requirements, to achieve the "static" and "dynamic" standards, at the same time, the zone should also be dynamic monitoring of micro-organisms (planktonic bacteria, bacteria, surface micro-organisms).
Microorganisms mainly include viruses, rickettsiae, bacteria, fungi and protozoa, etc., and the main ones related to cleanrooms are bacteria and fungi. Bacteria cannot survive alone, so it is possible to block dust particles through primary, intermediate, and (sub)high efficiency filtration of air conditioners, which also accomplishes the blocking of bacteria. For sterile areas, microbial testing is more important, but the cycle time for direct testing is long. Therefore, particle levels can be used as an indirect measure of their specific condition. These two aspects of the test can be for the aseptic production process environment of the degree of destruction and sanitation for the assessment of the final product release to provide data support.
3、Methods and points to note for dynamic monitoring
3.1 Suspended particles
At present, the determination of suspended particles is mainly microscope method and automatic particle counting method, and the instruments used for monitoring suspended particles in clean area air are mostly light scattering particle counters and laser particle counters. To summarize the actual situation, it is recommended that a continuous monitoring system be used to detect airborne particles in Class A zones. The online monitoring system can provide real-time feedback of the monitoring information so that the supervisors can propose timely solutions to the problems. For example, to remind the operator to slow down the action amplitude, to provide a basis for environmental cleaning, disinfection, downtime waiting and other production process control. At the same time, but also for the daily inspection and maintenance of air conditioning filters to establish a set of perfect operation, testing, replacement procedures. Only by doing so can the risks involved be effectively controlled.
3.2 Floating bacteria
Planktonic bacteria samplers are often monitored using the slit sampler in the impingement method, where air is extracted through a porous lid while microorganisms in the air stream impinge on the surface of the agar medium attached to a standard petri dish. Normally, when determining planktonic bacteria, the sampling volume of each sampling point should not be less than 1m3, while in the production process, the sampler can be set up to monitor the whole production process by using the interstitial way of sampling, waiting, and re-sampling. In addition, the planktonic bacteria sampler also has sieve hole impact type, surface vacuum sampling, centrifugal type, filtration type and liquid impact type and other sampling methods.
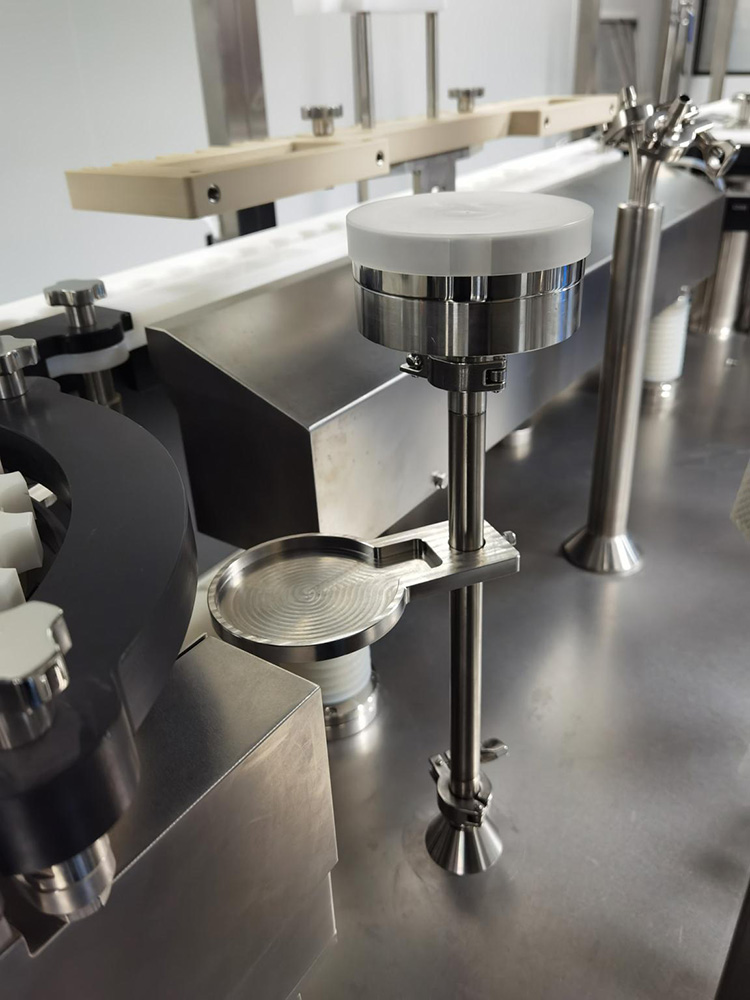

Filling line plankton sampling diagram
3.3 Sedimentation bacteria
Sedimentation bacteria are collected by the exposure method of live biological particles landing in the petri dish, and their culture, reproduction and counting. The petri dish for sedimentation bacteria determination should be arranged in a representative place and the place where the air flow disturbance is minimized. Specific sampling methods and incubation methods involve placing the petri dish close to operating height and then opening the outer lid and placing it upside down to expose the surface of the culture medium. In static monitoring, the petri dish should be left for not less than 30 min before the lid is closed for collection;in dynamic monitoring, the exposure time should be verified according to both the dish itself and the environment, and the exposure time of a single dish can be less than 4 h, but not more than 4 h. In the same location, several dishes can be used for continuous monitoring and cumulative counting, and then collected, and the yeast and mold are usually collected under the condition of 20~25 ℃. Yeasts and molds are usually counted after 5-7d incubation at 20-25 ℃, while aerobic bacteria are usually counted after 48-72h incubation at 30-35 ℃. Sedimentation disks are widely used in clean area environmental testing for their advantages of being inexpensive, lightweight, and less destructive to the air environment. However, when using a sinker dish, the exposure time of the dish should be confirmed first (note down the time when the petri dish is opened and ended) to ensure that the medium will not affect the normal growth of microorganisms due to the loss of water, etc. after exposure. At present, a lot of manufacturers of petri dishes is the factory's own preparation, sealing is not as strong as the purchased petri dishes, in the production process, transit will be contaminated petri dishes themselves, so that the results obtained false positive. Therefore, it is recommended that a blank control of the petri dish itself should be used or a petri dish with good sealing should be purchased during the production process to improve the credibility of the test results.
3.4 Microbiological Testing of Object Surfaces
Object surface microbial testing can determine the level of microbial contamination on the surface of objects (including work clothes). In general, three methods can be used:indirect sampling with cotton swabs followed by incubation, direct contact sampling and surface rinsing. When utilizing the direct contact method, the contact dish used should be placed at room temperature and then used.
3.4.1 Swabbing Surface Sampling Methods
The sampling area for the swab wipe surface sampling method is generally 25 cm2, and human surface wipes should include at least the fingerprints of both hands, head, mask, shoulders, forearms, wrists and legs. Swab indirect sampling is suitable for irregular surfaces. When sampling, hold the swab handle in your hand, contact the sampled surface at a 30°angle, and use an S-or Z-shaped slow and rotate the swab to fully wipe. If the swab head is a calcium alginate material, use a dilute hydrochloric acid solution as a diluent (e.g., sodium citrate solution with a mass fraction of 1%) so that the swab head can be completely dissolved.
3.4.2 Direct contact method
The direct contact method is to contact the contact disk directly with the surface of the object to be sampled, the contact time is usually about 10s, and the colonies will grow after the culture. Because this method is easy to operate and can be quantified, it is widely used. However, this test is only applicable to flat and smooth surfaces, which are usually sampled before filling or clearing after filling. After sampling, the sampled surface is wiped with a gauze moistened with 75% ethanol to remove residue. The sampled and labeled contact discs are placed in an incubator for incubation. The incubator parameters are generally set at 30-35 ℃ and counted after 72h of incubation.
3.4.3 Surface rinsing method
Surface rinsing method is suitable for monitoring the microbial bacterial content of surfaces in large areas, including equipment rails, water storage tanks, etc. The surface is rinsed with a quantitative amount of sterile water, the rinse water is collected, and the number of microorganisms is counted by the membrane filtration method.
3.5 Wind Speed Test
The wind speed in the Class A area during the production process, so that the wind speed of the production environment meets the guideline value (0.36~0.54 m/s), and at the same time, it can also determine whether the laminar flow is open, whether it is running normally, whether it is blocked or leaking, so that the production environment meets the requirements. At present, since the installed isolators are well sealed, the laminar air velocity can also be appropriately reduced after appropriate verification. Some of the literature states that a positive pressure sterile turbulent flow pattern can be selected for Class A areas, and that it is not always necessary to select a laminar flow pattern.
3.6 Isolation Operator Glove Testing
At present, the testing of gloves is generally used integrity testing, applying a certain pressure to its internal, in the specified time, the pressure reduction value in the acceptable range is considered to be qualified. In addition, it is also possible to increase the visual inspection program of gloves before and after each shift of production, etc. Detection cycle should be based on the characteristics of the product, equipment and shift arrangements and other factors to verify the results.
4, daily monitoring of sampling points and sampling frequency
The location of the most critical points as a sampling point is not necessarily applicable, so it must be considered whether environmental monitoring will increase the probability of product contamination risk. For example, the sampling point of suspended particles, generally arranged at a distance of 0.8 ~ 1.5m from the ground, try to avoid sampling near the return air outlet, and the tester should stand on the downwind side of the sampling port. The sampling points and sampling volume in the clean zone monitoring can be less than those in the clean zone level confirmation, and the sampling points are determined through validation, and they should be analyzed through risk analysis and monitoring results (at least 6 months of operation data as the basis for analysis). The issue of monitoring frequency is also a subject worthy of deep thought;insufficient monitoring frequency does not reflect well the problems involved -too much monitoring frequency is not conducive to resource optimization. Therefore, the frequency of monitoring is generally determined using the risk value distribution (RNR), which is the product of the severity of risk occurrence (SEV) and the likelihood of risk occurrence (OCC). Different monitoring frequencies are determined according to the magnitude of the risk value, and practical measures are also established to reduce the risks involved.
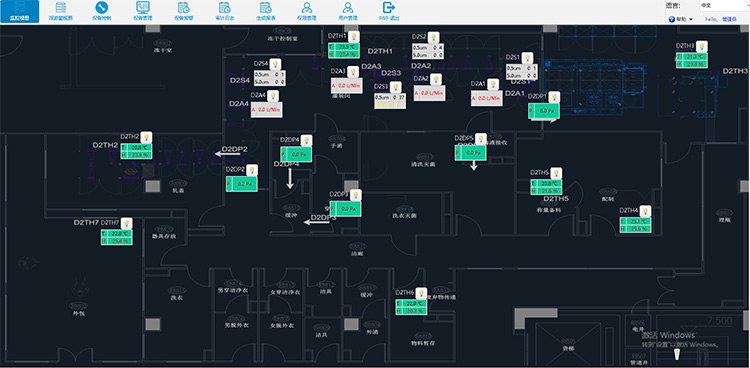
Daily Software Monitoring Diagram
5. General Exceedance Handling Methods and Report Printing
During the daily monitoring process, if there is a deviation in the monitoring data, the data will be higher than the set limit, so it is necessary to investigate what happened and how to prevent the problem from recurring through CAPA (Preventive and Corrective Actions), and the deviation and its follow-up measures must be recorded accordingly. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the problem from six aspects:man, machine, material, method, environment and measurement, and use risk assessment tools to investigate the risk points, find out the main causes, and formulate practical measures to solve the problem, and at the same time, it is also possible to do the necessary training, appraisal and evaluation work in order to solve the problem at the root. During the daily monitoring process, each batch report should be printed out and attached to the production record of the corresponding batch. The production time can generally be divided into four stages:preparation, self-purification, production and clearing, however, the report should be printed out to include the self-purification time of the environment and the production time, and a note should be made to explain the monitoring of the results of the exceedance and the exceedance of the standard, so as to ensure the traceability of the production of the product.
6. Conclusion
With the increase of drug supervision and the enhancement of market requirements, drug manufacturers need to strictly control the whole production process, especially the whole production process of sterile drugs. The application of automation technology makes unmanned operation of drug production line gradually possible;the use of sterile isolator makes unmanned operation of key processes possible. However, there are still some shortcomings in the use of isolation operators in China, such as online monitoring of the process of putting in and taking out petri dishes, difficulties in the implementation of online replacement of gloves, and the lack of emergency measures when there is a leak in the system. For these problems, more systematic research is needed. Meanwhile, the application of dynamic monitoring system can provide real-time data and alarm information, which is convenient to control the production process in time and take effective means to solve the problems in the production process. In addition, the application of online monitoring system can reduce the pollution caused to the production environment and ensure the quality of products.
Shenzhen ESKY cleanrooms Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the dynamic monitoring system of suspended particles and planktonic bacteria in aseptic laboratories and aseptic production workshops, and provides online monitoring systems for leading pharmaceutical companies in China, such as Beijing Kexing and Wuhan Institute of Biological Sciences, etc. We are not only an excellent agent of scientific instruments, but also an excellent supplier of online monitoring integrated systems.
















 Home
Home Product
Product News
News phone
phone