GB/T 25915 "Clean Rooms and Related Controlled Environments-1: Air Cleanliness Level" was released and will be implemented on March 1
- 2023-02-07
- 1808
- Esky Purify
Recently, the National Standards Commission issued GB/T 25915.1-2021 "clean room and related controlled environment-1: air cleanliness level", the document modifies the use of ISO 14644-1 :2015 "clean room and related controlled environment Part 1: air cleanliness level according to the concentration of particles," which will replace the GB / T 25915 .1-2010 "clean room and related .1-2010 "Cleanrooms and Related Controlled Environments Part 1: Air Cleanliness Classes by Particle Concentration", which will replace GB/T 25915 .1-2010 "Cleanrooms and Related Controlled Environments Part 1: Air Cleanliness Classes" and will be implemented on March 1, 2022
The interpretation of the document is as follows:
On the cleanliness test sampling point number of requirements, the document deleted based on the area of the calculation of the number of sampling points of the formula, but in advance to give a different room area corresponding to the number of sampling points of the table:
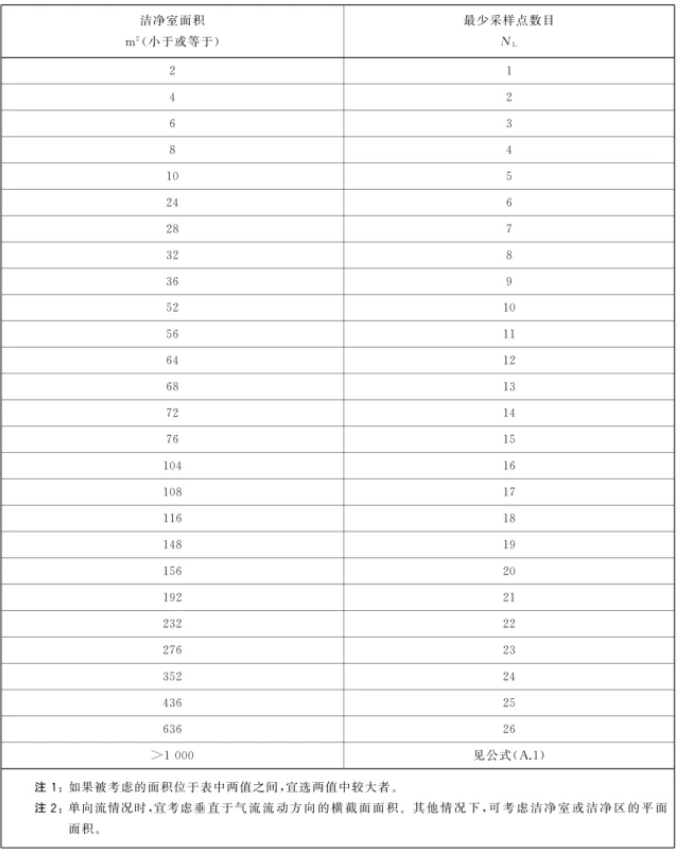
For room areas ≥636 sq. ft. (>1000 sq. ft. for ISO14644:2015), the calculation is done by the following formula (the formula is different from ISO14644:2015):
. Removal of the requirement to perform UCL/LCL calculations for particle concentrations
The document gives a method for determining the volume of a single sample and the sampling time at each point: the concentration of particles of the largest size selected is exactly at the upper limit of the specified ISO level, and the volume of air collected at each sampling point is sufficient to detect at least 20 particles. The single sampling volume VS for each sampling point is calculated according to equation (A.2).
Each sampling point of the sampling volume of at least 2L, each sampling point of the minimum sampling time for a single sampling 1 min, each sampling point of each sampling volume should be consistent.
The following is a summary of the requirements of ISO 5 (Class A). Deletion of ISO 5 (Class A) 5.0um particle limits:

. Regarding monitoring instruments (particle counters), calibration is required in accordance with GB/T 29024.4-2017 (equivalent to the adoption of ISO 21501-4:2007, while the latest version of ISO is ISO 21501-4:2018).
. The document will be implemented on 3/1/2022.
Full text:

1Scope
This document specifies the air cleanliness level in the clean room, clean area, and isolation device described in GB/T25915.7 according to the concentration of suspended particles in the air.
This document applies to the particle size lower limit of 0.1μm~5μm of the cumulative count distribution of particles and its particle concentration monitoring.
Particle concentrations of ultrafine particles (5μm) are quantified using the M descriptor.
This document does not apply to the characterization of airborne particles. This document is not intended to characterize the physical, chemical, radiological, biological or other properties of airborne particles.
2 normative references
The content of the following documents through the normative references in the text and constitute the essential provisions of this document. In the case of dated references, only the version corresponding to that date applies to this document; in the case of undated references, the latest version (including all change orders) applies to this document.
3 Terms and Definitions
3 Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this document.
3.1 Basic
3.1.1
洁净室 cleanroom
A room in which the concentration of suspended particles in the air is controlled and graded, and the design, construction and operation of the room are all controlled so that particles enter, are generated and remain in the room.
The room is designed and constructed to control the entry and retention of particles. Note 1:Provides levels by airborne particle concentration.
Note 2: May also affect the cleanliness level of other factors, such as airborne chemicals, microorganisms or nano-scale particle concentrations, as well as affecting the surface cleanliness, etc.
level of other factors, such as airborne chemicals, microorganisms or nanoscale particle concentrations, and so on. 级的其他因素,如粒子、纳米粒子、化学物或微生物浓度等,作出规定并进行控制。
Note 3: Temperature, humidity, pressure, vibration and static electricity and other related physical parameters can also be controlled as required.
3.1.2
Cleanzone
cleanzone
3.1.2
Note 1:The level of airborne particle concentration has been determined.
Note 2: Can also affect the cleanliness level of other factors, such as airborne chemicals, microorganisms or nano-scale particle concentration, as well as the impact of surface cleanliness and other
level of other factors, such as airborne chemicals, microorganisms or nano-scale particle concentration, as well as the impact of surface cleanliness
级的其他因素,如粒子、纳米粒子、化学物或微生物浓度等,作出规定并进行控制。
Clean zone Note 3: The clean zone can be limited to the clean room space, can also be used to isolate the device to achieve. Isolation device can be located in the clean room can also be outside the clean room.
; The clean zone can be limited to the clean room space, can also be used to isolate the device is located in the clean room or outside the clean room. Note 4: Temperature, humidity, pressure, vibration and static electricity and other related physical parameters can also be controlled as required.
3.1.3
Facilities instalation
; s Facility instalation
A clean room or one or more clean areas with all associated structures, air handling systems, supplies and utilities.
3.1.4
Classification
3.1.4
Cleanliness level of a clean room or clean area. Note: The cleanliness level should be described by the ISO class concentration, which represents the maximum allowable particle concentration per unit volume of air.
3.2 Airborne particles 3.2 Airborne Particles
3.2.1
3.2.1
Particle particle
A tiny substance with a defined physical boundary.
3.2.2
Particle size particlesize
The diameter of a sphere measured by a given particle sizer that is comparable to the response of the particles being measured.
The diameter of the sphere, as measured by the given particle sizer, is comparable to the response of the particle being measured. Note:The light scattering discrete particle counter gives the optical equivalent diameter.
3.2.3
3.2.3
Particle Concentration particleconcentration
The number of particles per unit volume of air.
3.2.4
Particle Size Distribution particlesizedistribution
; The concentration of particles as a function of particle size, expressed as a cumulative distribution.
3.2.5
Large particles macroparticle
Particles with an equivalent diameter greater than 5μm.
3.2.6
M descriptor Mdescriptor
Measured or specified concentration of large particles per cubic meter of air, where the equivalent particle size is related to the measurement method.
The M descriptor can be used to describe a particle. Note: The M descriptor can be regarded as an upper bound on the mean value of the sampling point. The M descriptor cannot be used to represent an ISO cleanliness level, but the M descriptor can be referenced on its own or in conjunction with an ISO cleanliness level.
3.2.7
Unidirectional Airflow Unidirectional airflow
Unidirectional airflow
Unidirectional flow A controlled airflow that passes through the entire cross-section of a clean room or clean area with a steady and parallel wind speed.
Controlled airflow through the entire section of a cleanroom or clean zone with a constant and parallel air velocity. 3.2.8
Non-unidirectional Flow Non-unidirectional airflow
The clean room or clean area of the air supply in an induced manner with the indoor air mixing airflow distribution.
3.3 Occupancy state
3.3.1
Empty-state as-built
Clean room or clean area all services and facilities in place and running, but no equipment, furniture, materials and personnel state. 3.3.2
Static at-rest
A state in which a clean room or clean area is completed and equipment is in place, operating in an agreed-upon manner, but with no personnel present.
3.3.3
Dynamic operational
Dynamic Operational
The state in which a clean room or clean area facility is operated in an agreed-upon manner, and a specified number of personnel are working in an agreed-upon manner.
Clean room or clean area facilities in accordance with the agreed manner of operation, and a specified number of personnel in accordance with the agreed manner of work. 3.4 Testing instruments
3.4.1
3.4.1
Resolution
Resolution The smallest variable that can be measured, i.e., a recognizable change in the corresponding display.
The smallest variable that can be measured, i.e. the recognizable change in the corresponding display. Note: Factors such as noise (internal or external) or friction can determine the resolution, as can the value being measured.
[Source: ISO/IEC 17025]. [Source: ISO/IEC Guide99:2007, 4.14]
3.4.2
3.4.2
Maximum permissible measurement error maximum permissiblemeasurement error
3.4.2
For a specific measurement, or on the measuring instrument or measurement system, relative to the known reference value, technical conditions or specifications allow the measurement error extreme value.
; The measurement error of a specific measurement, or on the measuring instrument or measurement system, relative to a known reference value, the technical conditions or specifications allow the extreme value of the measurement error. Note 1: In the case of two limit values, usually with the term “Maximum permissible error” or “Error limit” to distinguish.
Note 2: “Tolerance” may not be used to indicate “maximum allowable error”.
[Source:ISO/IEC Guide99:2007,4.26]
3.5 Instrument specifications
3.5.1
Light scattering (discrete) airborne particle counter; LSAPC
3.5.
nbsp; ; Light scattering (discrete) airborne particle counter; LSAPC An instrument for counting and sizing individual airborne particles based on their optical equivalent diameter.
& nbsp; The instrument counts and sizes individual particles in the air according to their optical equivalent diameter. Note: GB/T29024.4—2017 gives the specification of LSAPC.
3.5.2
discrete-macroparticlecounter
3.5.2
An instrument that counts and sizes individual large particles in the air.
The instrument is capable of counting and sizing single large particles in the air. Note:The technical specifications are shown in Table F.1 in Appendix F.
3.5.3
Time-of-flight sounder time-of-flight sounder Time-of-flightParticlesizingapparatus
Time-of-flightparticlesizingapparatus
Time-of-flightparticlesizingapparatus
Discrete particle counting and sizing devices.
Note 1:The travel time of a particle after a change in fluid velocity is usually measured with the help of optical methods. Note 2:The technical specifications of the device are as follows.
Note 2:Its technical specifications are shown in Table F.2.
4 Grading
4.1 Occupancy Status
Should be provided in “ empty state ” “ static ” and “ dynamic ” a certain state or states of occupancy (see 3.3), on the clean room or clean area by the Airborne particle concentration classification. 4.2 Particle size
When the air cleanliness classified by particle concentration, the range of 0.1μm ~ 5μm one or more particle size blocking threshold (low value).
4.3 ISO Classification Number
Air cleanliness by particle concentration shall be labeled as ISO Class N. The maximum permissible concentrations for each particle size of concern are shown in Table 1.
The number of particle concentrations at different particle size thresholds in Table 1 is only used as a grading criterion, and does not reflect the true size and number distribution of particles in the air. Appendix B lists several classifications.
A few examples of grading calculations are shown in Appendix B.
Table 1 Air Cleanliness ISO Classes by Particle Concentration & nbsp;;
4.4 Representation method & nbsp;
The method of expressing the concentration of suspended particles in a clean room or clean area shall include: ; 4.4 Method of expression 4.5 Methods of expression
a) the number of ISO classes expressed as “ISO N class” .
b) Occupancy status at the time of grading;
c) Focus on particle size. c) Attention to particle size.
If there is more than one particle size of concern, the larger particle size (D2) should be at least 1.5 times the size of the next smaller particle size (D1), i.e. D2≥1.5×D1. c) Focus on particle size. amp;nbsp;
See Table 2 for examples. & amp;nbsp;
Table 2 Example table of particle sizes of concern
4.5 Non-integer Cleanliness Levels and Particle Size Thresholds When a non-integer level is required, the particle size thresholds should be set at the level of the cleanliness level.
When non-integer grades are required, or when integer and non-integer grades are required for particle size stops not listed in Table 1, see Appendix E. .
5 Proof of Conformity 5.1 Principle
5.1 Principles 5.2.1.1 The following are the principles of the test program.
Completion of the required testing procedures, and provide testing conditions and results of the relevant documents, in order to certify compliance with the user-specified air cleanliness (ISO class number) requirements. Static and dynamic grading is usually done in the same way.
Static and dynamic grading is usually done annually based on a risk assessment. Static and dynamic ratings are usually done annually based on a risk assessment.
The monitoring of clean rooms, clean areas and isolation devices should be in accordance with GB/T25915.2—2021. .
Note: Facilities equipped with continuous or frequent monitoring of particle concentrations and other performance parameters of the instrument, if the monitoring results remain within the specified monitoring limits, the graded detection interval can be extended. 5.2 Detection
5.2 Tests The compliance tests are given in Appendix A.
The baseline methods for compliance testing are given in Appendix A, and other methods and/or instruments of at least equal accuracy may be specified. If no alternative method is specified or agreed upon, the reference method shall be used. ; The calibration should be used within the validity period of the calibration.
The compliance testing should be performed with instruments within the calibration validity period. 5.3 Calculation of Suspended Particle Concentration
5.3 Calculation of Suspended Particle Concentration The test shall be conducted in accordance with Appendix A after completion of the test.
According to Appendix A after the completion of the test, each sampling point of a single sampling volume of particle concentration (expressed in terms of the number of particles per cubic meter) should not exceed the concentration limits in Table 1 in the corresponding particle size or Table E.1 in the corresponding particle size of the non-integer level of the concentration limit. If multiple samples are taken at a sampling point, the concentrations shall be averaged and the average concentration shall not exceed the concentration limits given in Table 1 or Table E.1. Non-scheduled particle sizes shall be calculated by equation (E.1).
For the purpose of determining the ISO class, the concentration of all particles of concern should be measured by the same method. For determining the ISO class, the same method should be used for all particles of concern.
5.4 Detection report Clean room or clean area.
Each clean room or clean area test results should be recorded, submitted in the form of a comprehensive report, and whether it complies with the provisions of the air cleanliness classified by particle concentration. Test report should include the following.
The test report should include the following:
The name and address of the testing organization and the date of completion of the test;
The number of this document, such as ;
Clearly indicate the actual location of the measured clean room or clean area (including adjacent reference area, if necessary) and all the coordinates of the sampling point (should be accompanied by a map); .
Provide a clean room or clean area representation, including ISO class number, the relevant occupancy status and particle size of concern; ;;;;;
Detailed description of the test method, including any special conditions associated with the test or deviations from the test method, as well as the model number of the test instrument and current calibration certificate; and
Test results, including particle concentration data for all sampling points; and
If the concentration of large particles has been quantified as described in Appendix C, the information should be included in the test report.
APPENDIX A
(Normative)
Benchmarking Methods for Classifying Air Cleanliness by Particle Concentration
A.1 Principle
A discrete particle counter is used to measure the concentration of airborne particles greater than or equal to a specified particle size at a designated sampling point.
A.2 Instrument Requirements A.2.1 Particle Counters
A.2.1 Particle Counter
Particle counter should have the ability to distinguish particle size, can display or record the number of particles in the air and the size of the particle size, can be based on the cleanliness level, the determination of the total concentration of particles within the appropriate size range. ; The particle size of the air can be displayed or recorded, according to the cleanliness level, to determine the total concentration of particles in the appropriate size range.
Note: Light scattering (discrete) airborne particle counters are commonly used for air cleanliness classification testing. &

















 Home
Home Product
Product News
News phone
phone